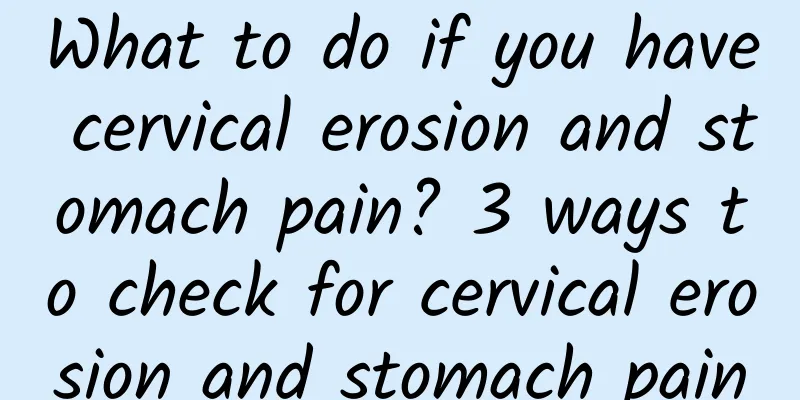
Mechanism of dysfunctional uterine bleeding caused by sex hormone secretion disorder

|
The normal menstrual cycle is a biological clock phenomenon. It is affected by internal and external environmental factors and regulated by neuroendocrine, so that female reproductive physiology and reproductive endocrine function follow strict biological rhythms. Sex hormone secretion disorders can lead to menstrual disorders and abnormal uterine bleeding. Anovulatory Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding Single and long-term estrogen stimulation causes progressive hyperplasia and proliferation of the endometrium, leading to highly cystic and adenomatous hyperplasia, and even progression to endometrial cancer. Due to the lack of progesterone antagonism and glandular secretion, the endometrium is thickened, the glands increase, the glandular cavity is enlarged, and the glandular epithelium proliferates abnormally. The blood supply to the endometrium increases, and the spiral arterioles are tortuous. The polymerization and gelation of acid mucopolysaccharides (AMPS) caused by estrogen reduce the permeability of blood vessels in the interstitium, affect material exchange, cause local endometrial tissue ischemia, necrosis and shedding, and cause bleeding. The coagulation of AMPS also hinders the shedding of the endometrium, causing asynchronous exfoliation of the endometrium, resulting in long-term irregular bleeding of the endometrium. Ovulatory dysfunctional uterine bleeding In patients with ovulatory functional uterine bleeding, the corpus luteum degenerates prematurely, resulting in a short luteal phase, frequent menstruation or incomplete atrophy, and continuous secretion of progesterone, leading to premenstrual bleeding, prolonged menstruation, and continuous spotting, or both. The mechanism is: insufficient secretion of estrogen and progesterone, especially insufficient secretion of progesterone, which makes the endometrium completely secreted, the glands, stroma and blood vessels are immature, and due to the asynchronous withdrawal of estrogen and progesterone, irregular exfoliation of the endometrium and abnormal bleeding are caused. |
<<: What are the surgical treatments for uterine fibroids?
>>: Patients with ovarian cysts should avoid cyst rupture
Recommend
Can vaginal candidiasis only be relieved
Is it true that candidal vaginitis can only be re...
How to use medicine in the early stage of cervical precancerous lesions
Cervical precancerous lesions are one of the more...
What are the dangers of irregular menstruation?
It is very common for women to have irregular men...
Fat everywhere? Eating potatoes can help with weight management
After a long vacation, many people are troubled b...
What are the symptoms of 2nd degree uterine prolapse
What are the symptoms of 2nd degree uterine prola...
How to Eat Reasonably for Patients with Uterine Effusion
We all know that diet is very important after we ...
What are the preferred hospitals for treating cervical warts?
Sitting and waiting for death is not an option fo...
What are the essential drugs for treating hyperprolactinemia?
Hyperprolactinemia is also known as hyperprolacti...
A powerful tool for quickly losing visceral fat! Protein-lipid diet: Lose 14 kg in 1 year
The "Protein-Lipid Diet" that can elimi...
How much does it cost to treat cervical warts?
For patients with high-risk cervical warts, the c...
Can people eat lychees after abortion?
You can generally eat lychees in moderation after...
Symptoms of ovarian cysts are mostly caused by ovarian tumor torsion
In order to better treat the symptoms of ovarian ...
How long can you live with Bartholinitis?
Bartholinitis is an inflammation caused by infect...
Experts teach you how to prevent cervical erosion
As a common gynecological disease, more and more ...
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a serious condition
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is an important ...