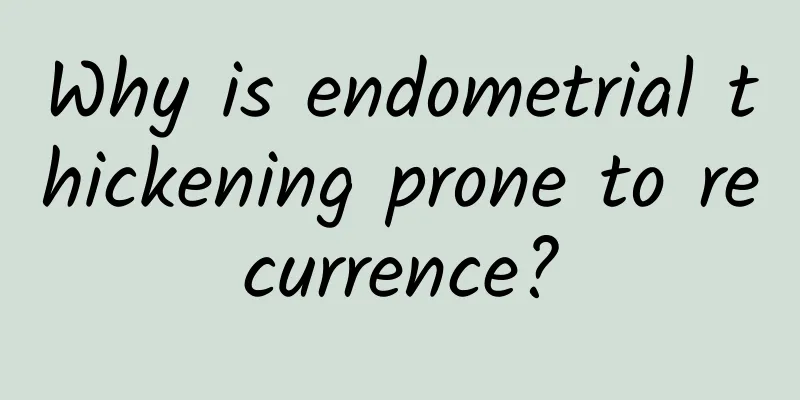
What does cervical warts look like?

|
With the liberalization of sexual concepts and changes in lifestyle, the probability and number of women suffering from cervical warts are also increasing. Women infected with this disease should also pay attention to it. Delaying treatment will only make the condition worse or even cancerous, and there is also a risk of transmitting the disease to others. Below, the editor will take you to understand its causes and symptoms. The picture below is a real picture of cervical warts to help everyone understand the symptoms. Genital warts are small, gray or skin-colored bumps that grow on or near the genitals. They are one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. They are caused by several strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). Warts usually appear near the vagina, vulva, urethra, cervix, penis, throat, or anus. Sometimes, they are so small and flat that you may not notice them right away. They may be clumped together or look like cauliflower. You may experience itching, bleeding, burning, or pain. But genital warts often take months or years to become noticeable, if they are present at all. Your doctor will decide whether your genital warts require treatment with medication, cryotherapy (freezing the warts to remove them), surgery, or acid solutions. Who is at risk? Anyone who is sexually active can get or spread HPV. Some things can make you more likely to get genital warts. They include: Having more than one sexual partner (or partners who do) Pregnant Have a weak or compromised immune system Smoking There is one vaccine for people ages 9 to 26. You can get three shots given over 6 months. Or, you can get the same protection from two shots as long as you take both before age 15. You have to get the pic before you were exposed to HPV for it to work. The vaccine won't protect you if you've already been infected with certain strains of HPV, and it won't protect you against all types of HPV. How do women get cervical warts? 1. Cervical warts are mainly transmitted through sexual contact, and unclean sexual life is the leading factor in infection of cervical warts. 2. Low immunity. This mainly refers to people with low immunity coming into contact with items with secretions from patients with cervical warts, which can cause the disease. For example, bath towels, bathtubs, foot basins, toilet seats, etc. with secretions from patients with warts can all become the medium for the spread of cervical warts. 3. Traumatic infection. The wart virus enters the human body through small broken wounds on the skin or mucous membranes and reproduces. When the virus reproduces to a sufficient number, it will cause the infected person to become ill. 4. Suffering from other sexually transmitted diseases. The pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases such as genital herpes, gonorrhea, syphilis, and AIDS can damage the human mucosal barrier, reduce the body's ability to resist genital warts viruses, and increase the risk of infection. What do cervical warts look like? 1. In the early stages of the disease, small cone-shaped fleshy papules will appear on the patient's labia majora and minora, vaginal opening, clitoris, vagina, cervix, perineum and perianal area. In a few patients, the mouth, armpits, breasts, and between the toes will also develop. Most of them are pink and cauliflower-shaped, with a brittle surface that can be easily removed by hand. They are also prone to bleeding and infection. 2. Cervical warts with obvious symptoms also manifest as: initially pink or red papules or rice-sized warts, which will gradually increase in size and number over time, merging into nipple-like, cauliflower-like or cockscomb-like growths, which can reach more than ten centimeters in diameter. Some may be the size of cauliflower, with a white, gray or pink surface, and will cause itching, burning pain and a foul odor. 3. In the early stage, if the symptoms of condyloma acuminatum are not obvious, there will be uncomfortable symptoms such as vulvar itching, burning pain or pain after sexual intercourse. Multiple squamous epithelial hyperplasia, at first there are scattered or clustered pink or white small papillary warts, which are soft and have fine finger-like protrusions. After enlargement, they become cockscomb-shaped, cauliflower-shaped, and mulberry-shaped. 4. If the disease develops to a very serious level, it will also cause cancer, such as cervical cancer. The probability of cervical warts becoming cancerous is proportional to the degree of development of the disease. Only when the disease deteriorates to a certain extent will a malignant tumor appear, and then the wart cells will become cancerous. Under normal circumstances, the probability of genital warts becoming cancerous is very small. |
<<: If a woman with endometriosis wants to get pregnant, is it good or difficult?
>>: How to treat uterine fibroids? Taking these Chinese medicines can cure them
Recommend
Effective prevention of dysmenorrhea in daily life
Among gynecological diseases, dysmenorrhea is one...
Ectopic pregnancy does not affect fertility again
For female friends who have experienced an ectopi...
Is it dangerous to go back to work right after an abortion?
It is dangerous for women with weak constitution ...
What should I do if my endometrium is thick? Can I get pregnant?
Does endometrial thickening affect pregnancy? Wha...
These four types of pelvic inflammatory disease examination items
Many people may not know much about the examinati...
How to check for pelvic inflammatory disease
How to check for pelvic inflammatory disease: The...
Symptoms and causes of female cervicitis Introduction to the three major treatment methods for female cervicitis
Cervicitis is a female gynecological disease that...
The best treatment for adenomyosis
There is currently no best treatment for adenomyo...
How to treat female adnexitis?
Adnexitis is a common disease caused by pathogeni...
What are the dangers of malignant uterine fibroids? Are malignant uterine fibroids serious?
What are the dangers of malignant uterine fibroid...
How to take the medicine for medical abortion? See what the doctor says
Medical abortion is also a common method of abort...
Crazy treasure hunting every day, office ladies get fat! Famous weight loss doctor: for decreased concentration
If you are keen on catching Pokemon, be careful n...
What to do if the menstrual blood clots do not come out and the lower abdomen hurts
What should I do if my lower abdomen hurts and th...
Causes and treatment of cervicitis
What are the causes of cervicitis? Experts from o...
How much does ectopic pregnancy surgery cost? It depends on the patient's physical condition
If the fertilized egg implants and grows outside ...